Osteochondrosis are degenerative-distribution disorders in the intervertebral joint cartilage tissue, causing its deformation and destruction.Osteochondrosis can develop in one or more spine.Osteochondrosis of the cervical regionIt occurs especially often and sometimes gives very serious complications.
Characteristics of cervical spine osteochondrosis
Due to the characteristics of the cervical spine structure, the course and the symptoms of osteochondrosis in this segment have several characteristics.The cervical spine consists of small movable vertebrae, which are constantly subjected to significant and long loads.The vertebral canal in the cervical region is the narrowest;Therefore, compression of the spinal cord in this segment develops much more often and leads to very serious injuries.In the neck, there is a large accumulation of nerve endings and blood vessels, including the vertebral artery, which provides cerebellum nutrition, the oblong brain and the back of the brain.The violation of blood flow in this artery leads to impaired coordination, dizziness, reduction of vision and hearing and, in severe cases, a stroke can be developed.
Symptoms of cervical spine osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical regionThe column is manifested by several syndromes:
-
Reflex and irrigation syndrome
The burning of pain in the cervical and consumed region, emerging after sneezing, sudden head movements or a long static state, for example, after sleeping or a fixed state and subsequent movement of the head or neck -Generally complaints with cervical spine osteochondrosis.Pain can radiate to the shoulder or thoracic cage. Spinal channel narrowing syndrome (spinal canal stenosis)
This syndrome develops as a result of the compression (tightening) of the spinal cord and its vessels, which leads to circulatory disorders in the affected area and the development of myelopathy - a rare but more formidable complication of osteochondrosis.Cervical myelopathy -carbon occurs mainly in medium and elderly people as a result of compression of the spinal cord or its vessels with posterior osteophytes, thick yellow ligament, intervertebral disc hernias.The disease develops gradually, at first, pain and restriction of movements in the cervical spine is observed.In the future, cervical osteochondrosis can cause impaired functions of the upper and/or lower ends, manifested by numbness, a tingling sensation in the fingers, a sensation of cotton or arms, until the development of paresis and paralysis-
Rook Syndrome
The manifestations of root syndrome in cervical spine osteochondrosis will depend on what compaction that the nerve root arose as a result of structural changes on the disc.However, in any case, cervical osteochondrosis will occur with painful, pulsating or burnt headaches, sometimes flowing into the type of hypertension.The back pain is rarely local and usually gives to shoulder blades, forearm, shoulder and/or hand, to the brush fingers.
Depending on the affected spinal segment, the following symptoms may be:
- C1-C2: Defeat in this segment, as a rule, occurs as a result of automotive injuries and manifests itself by a violation of smell and speech, hypotrophy of the facial and sublingual muscles and a decrease in sensitivity in the occipital region.
- C2-C3: It is also rarely affected and is accompanied by hearing, vision, and control of movement muscles and sensitivity, which leads to speech disorders and taste sensations, the appearance of a feeling of inflammation, perspiration or a nodule in the throat.
- C3-C4: How the diaphragmatic nerve retires in this segment, in addition to pain in the collarbone and shoulder GPU, belt spam and trapezoidal muscles, hypochondrium and heart pain also develop and breathing movements are disturbed.In addition, Gundaria, a feeling of nasal congestion, snoring, decreased smell, fallen muscles of the face, deterioration of teeth condition can develop.
- C4-C5: The defeat in this segment is accompanied by painful sensations on the shoulder of the shoulder, hypotrophy of the deltoid muscle, a decrease in the sensitivity of the external surface of the shoulder, shoulder and inflammation of the skeletal muscles in this area.Among other symptoms, changes in voice may occur, the feeling of inflammation in the larynx, snoring.
- C5-C6: The segment is most often susceptible to degenerative-distribution lesions and has extensive symptoms.First of all, the pain and impaired sensitivity of the shoulder blade skin, the external surface of the shoulder to the radial surface of the forearm and the thumb of the hand develops.Subsequently, the somatic symptoms develop, including frequent and little subject to the treatment of lungs and bronchi, including asthma, rheumatic and allergic manifestations, symptoms of angina shalters.
- C6-C7: The nerve roof injury in this segment leads to the appearance of pain in the scapula, the posterior surface of the shoulder, along the pre-judge surface of the forearm on the back of the hand.In addition, damage to this segment may accompany the symptoms corresponding to thyroid diseases, mediastinal organs and cardiovascular system.
- C7-T1: The C8 spine injury is accompanied by three-headed muscle hypertrophy and a pinky finger diverted, which leads to a weakening of the flexion reflex and pain with impaired skin, shoulder, shoulder, shoulder, elbow and dawn.In severe cases, symptoms can develop as in angina pectoris, arrhythmia and asthma.
-
Cardial syndrome for cervical osteochondrosis
Cardial syndrome develops with irritation of diaphragm innervated nerve roots (diaphragmatic nerve) or a large thoracic muscle.Symptoms are definitely identical to the attack of Angina Pectoris, but at the same time, the attack lasts in an unnatural way, the pain intensifies with a sharp head or neck movement, with sneezing or sharp cough.The standard coronary does not bring relief, and the ECG at the time of the attack does not show a violation of coronary circulation.At the same time, cardiac syndrome can be accompanied by tachycardia, arrhythmia and high blood pressure. -
Vail Artery Syndrome
This syndrome is one of the most frequent and dangerous manifestationsosteochondrosis of the cervical regioncolumn.This syndrome develops against the background of squeezing the vertebral artery and circulatory disorders in the corresponding areas of the brain (cerebellum, brain trunk and rear lobes), which determines the clinical picture.
One of the main manifestations of vertebral artery syndrome is a severe pulsating and/or burning headache, constant or paroxysmal, exciting darkness, excessive part, whiskey and back of the head.Usually the pain can be one side.In the early stages of development, headaches emerge or intensify after a long stay in an uncomfortable position with the head back, after physical effort, or after sudden movements.With the narrowing of the lumen, the artery of pain becomes more pronounced and frequent, sometimes constant.In severe cases or peak headache, vomiting may occur, a fainting state is not excluded.
The visual disorders of cervical osteochondrosis can occur separately and against the bottom of the headaches and expressed by the pain of the eyeball, of impaired visual acuity, a feeling of veil before the eyes, dryness or stove in the eyes.One of the characteristic symptoms of vertebral artery narrowing is sudden short -term dizziness or orientation losses in space.Such attacks occur for a few seconds and pass quickly.A sudden noise may occur in the ears or pulse in the head area.In addition, damage to the vertebral artery can lead to the development of cardiac syndrome.
In severe cases, an attack of an "ischemic attack", manifested by serious headaches, vomiting, loss of coordination of movement, a change in handwriting, marching, double, impaired discourse and balance, can develop.
Diagnosis of cervical spine osteochondrosis
The doctor can make the primary diagnosis of cervical spine osteochondrosis in the first examination of the patient, in addition to determining the level of the affected spine, anatomical characteristics, including posture, physical, body structure, spicy process line, side contours of the neck, the lower corner of the shoulder;Location, nature and degree of pain syndrome;The amplitude of the spine, relief and muscle tone.
The diagnosis is specified using visual diagnosis methods (radiographic studies, CT, RM), which allow the stage of the disease, the level of spine lesions, the precise location of the deformed disc.And based on these data, the most ideal treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is selected.
Treatment of cervical spine osteochondrosis
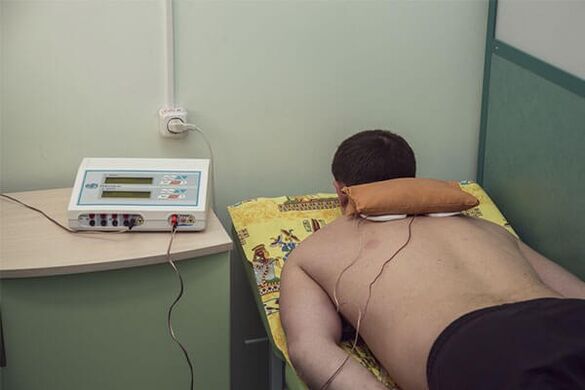
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, surgical and conservative methods are used.But surgical treatment is prescribed only in the presence of serious complications that occur in the posterior stages of osteochondrosis if:
- The spinal canal stenosis (narrowing) was formed;
- The vertebral artery is suppressed;
- A significant hernia or protrusion was formed, compressing the nerve roots;
- Excessive instability of the developed column.
In other cases, the treatment patternosteochondrosis of the cervical regionThe spine is conservative therapy.This is due to the fact that, with all the achievements of modern medicine, the consequences of surgical intervention are not always expected.
Conservative treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The best results in treatmentosteochondrosis of the cervical regionThe spine, as well as other types of osteochondrosis, are achieved when you see a doctor.Unfortunately, many patients usually do not attribute importance to mild discomfort in the rear or periodic headache.On the other hand, there are many cases of inappropriate diagnosis and long useless treatment, sinceOsteochondrosis of the cervical regionThe spine can simulate other diseases such as arthritis, myalgia or angina pectoris.This is why vertebrologists recommend checking the spine in the presence of symptoms of any diseases, especially accompanied by head pain or spine.
In the effective treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, an integrated approach is of great importance, including the following directions:
- Drug therapy- In order to improve intervertebral disk tropism and interrupt pain, remove muscle spasm and inflammation during exacerbation.For these purposes, non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs, painkillers, muscle relaxants and chondroprotectors are prescribed to stimulate the restoration of joint cartilage tissue, group B group's vitamins;
- physiotherapy- It is prescribed to reduce pain, improve disk cartilage nutrition, stimulate cartilage regeneration processes, remove muscle spasm, inflammatory processes in the post -operative period for rapid recovery;
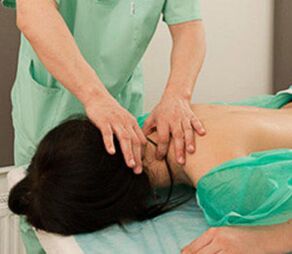
- Manual therapy- It is used to eliminate muscle cramps, reduce pain, improve blood and lymphatic metabolism, posture correction and improve joint amplitude.The manual exposure scheme is individually selected for each patient;
- massage-The widely used and well established method to treat musculoskeletal system diseases.It has the same effect as manual therapy;
- Medical Physical EducationIt is one of the most important methods for treating all types of osteochondrosis, including cervical spine osteochondrosis.The purpose of exercise therapy is to relieve muscle spasm and compression of nerve roots, improve blood and lymphatic flow in the spine, strengthen muscle structure and increase the flexibility of the ligament apparatus.For each patient, a set of exercises is selected, whose correct implementation is monitored by a specialist;
- ReflexologyIt refers to an alternative type of treatment, widely used today and provides a very good result in combination with other treatment methods.The essence of the method is the impact on acupuncture points and/or reflexogenic zones, in order to achieve the same results as with other therapeutic methods (reducing muscle pain and spasm, decompression of spinal brain roots, improving tissue trophies in vertebra) as well as to improve sleep, relying on psychomotional.
For the treatment of chronic osteochondrosis, chondroprotectors, group B vitamins (B6, B12) and external use medications are also used - ointments, creams, gels that contain NSAIDs, local agitation and tissue regeneration stimulants.
In addition to the main treatment methods, with cervical osteochondrosis, patients are recommended to alter the usual lifestyle, as, in most cases, the disease continues against low mobility, bad or malnutrition, obesity or, conversely, overly low and bad habits.In most cases, in the early stages of cervical osteochondrosis, it is sufficient to bring a healthy lifestyle, not allow muscle spasms and overload of cervical cervical region muscles, provide comfortable sleep conditions, normalize nutrition, and meet the recommendations of the doctor in exercise therapy to further development of pathological and continuous processes.



















